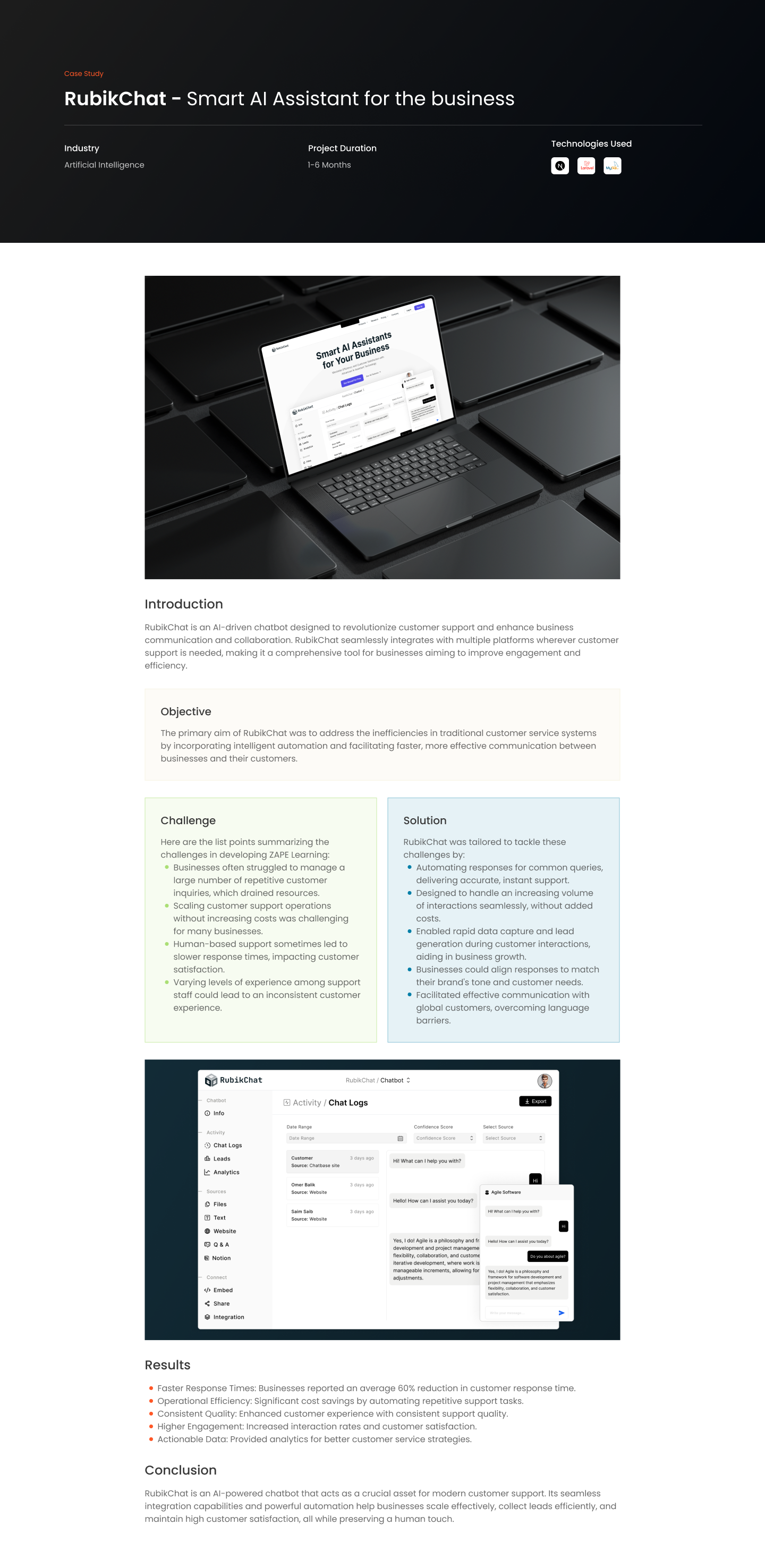
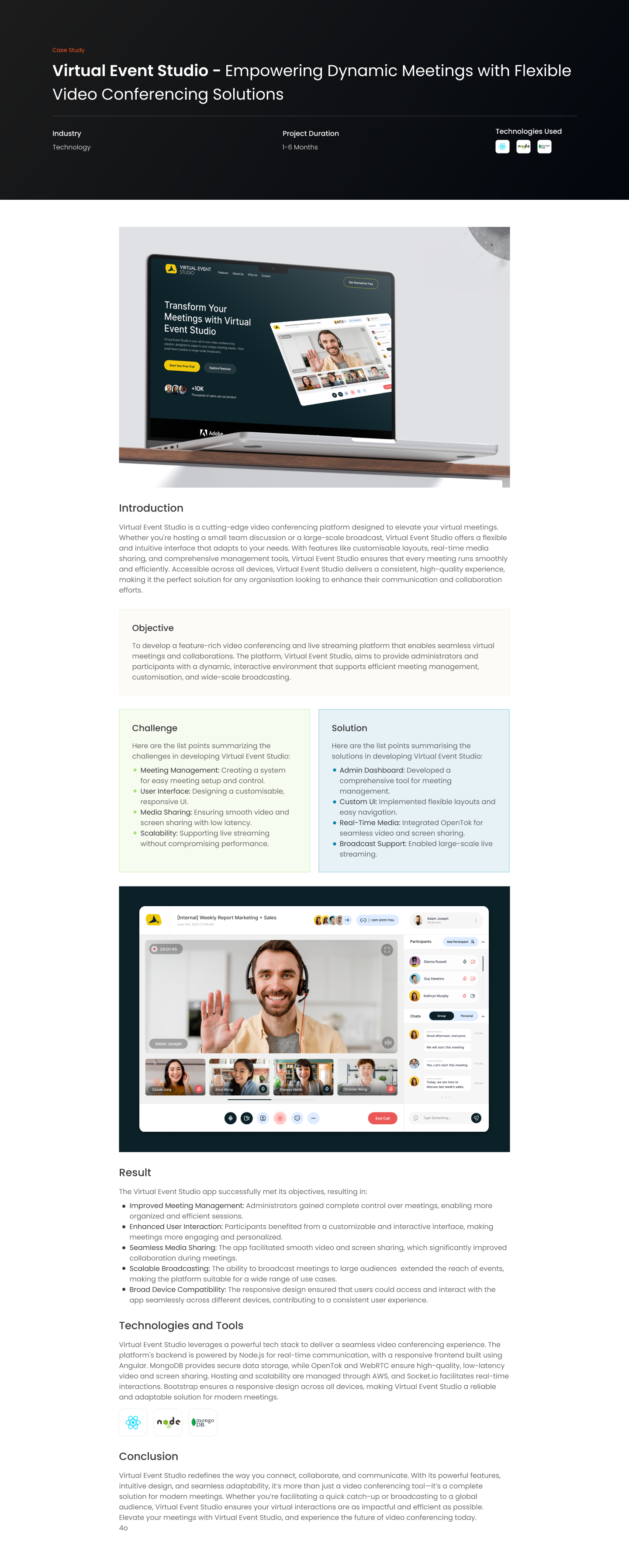
Introduction
This blog will unravel the complexities of Blockchain technology, exploring its foundational principles, varied applications, and how it’s paving the way for a secure and transparent digital future. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an investor, or simply curious about this revolutionary technology, this exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of Blockchain.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that maintains a secure and decentralized record of transactions across a network of computers. It is best known as the technology underpinning cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its potential applications extend far beyond.
Core Principles of Blockchain
1. Decentralization: Unlike traditional systems, Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for a central authority.
2. Transparency and Immutability: Every transaction on the blockchain is transparent and immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted.
3. Security: Utilizes cryptographic principles to ensure secure and tamper-proof transactions.
Applications of Blockchain
1. Cryptocurrencies: Digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security.
2. Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly written into lines of code.
3. Supply Chain Management: Enhances traceability and accountability in supply chains.
4. Voting Systems: Potential to create secure and tamper-proof digital voting systems.
5. Identity Verification: Provides a secure and unforgeable method of managing digital identities.
Benefits of Blockchain
1. Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud.
2. Increased Efficiency and Speed: Streamlines and automates processes.
3. Improved Traceability: Tracks the origin and journey of products and assets.
4. Reduced Costs: Cuts out middlemen and reduces transaction costs.
Challenges in Blockchain
1. Scalability: Handling a large number of transactions efficiently remains a challenge.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment surrounding blockchain is still evolving.
3. Technology Adoption: Integrating blockchain with existing systems poses technical and logistical challenges.
4. Energy Consumption: Particularly for proof-of-work systems, energy consumption can be significant.
Further Reading and Exploration
1. Advanced Blockchain Technologies: Explore emerging blockchain technologies like Ethereum 2.0, and learn about different consensus mechanisms like proof of stake.
2. Blockchain in Different Industries: Understand how blockchain is being applied in finance, healthcare, real estate, and other industries.
3. Cryptocurrency Deep Dive: Delve into the world of cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and altcoins, understanding their workings and market dynamics.
4. Blockchain and Cybersecurity: Learn about the role of blockchain in enhancing cybersecurity measures and protecting digital assets.
5. The Future of Blockchain: Stay updated with the latest trends and developments in blockchain technology and its potential future applications.